Supporting local implementation of NICE Technology Appraisal
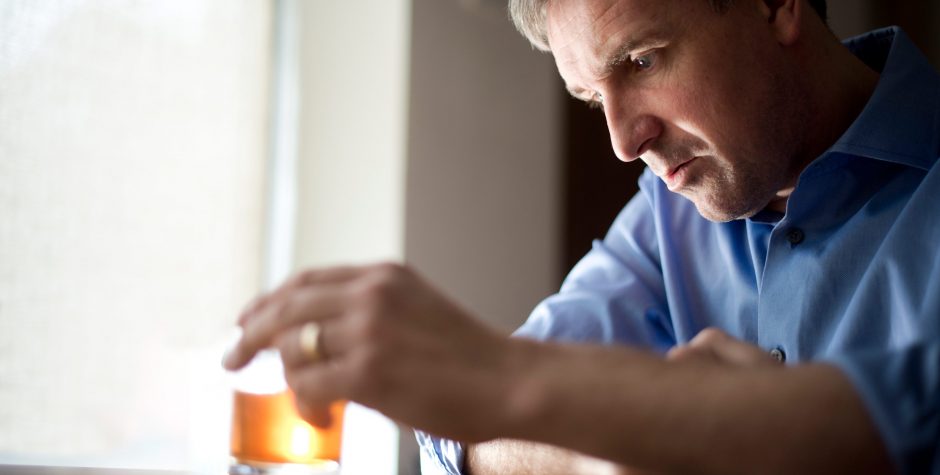
Alcohol dependence is now one of the biggest health problems facing the NHS today. In the past 40 years alcohol‑related deaths have risen over three-fold and alcohol is now the leading cause of death in men aged under 50 years, and it is likely that this trend will be replicated in women in the next decade. Since the formation of the NHS there have been only three pharmacological treatments with marketing authorisations for use in people with drinking problems—acamprosate, disulfiram, and very recently, naltrexone. These drugs are indicated to help maintain abstinence and have limited efficacy, in part because the almost universal consumption of alcohol by adults in the UK makes abstinence socially very stigmatising.